Mobile Data Entry Using RFID Devices in Warehousing – SAP EWM Perspective
Whether deployed as part of an ERP software package or as a standalone system capable of integrating with external ERP systems, a warehouse management system has become an essential instrument to optimize the inventory management and order fulfillment processes of warehousing, which is a crucial function of supply chains today.
- Speed, precision, and efficiency in data processing are the key factors for a successful warehouse management system.
- Speed in a warehouse management system is characterized by the amount of data that is processed, workflows that are automated, and transactions that are executed in each time frame.
- Precision is about how accurately the data is retrieved, recorded, and transmitted during workflows.
- Efficiency is gauged by the productivity achieved with the help of the functional support offered by the system.
Having a best-in-class warehouse management system like SAP’s EWM, which can optimize end-to-end business processes, is not of much help if the warehouse management fails to utilize the capabilities of such a system at an operational level.
The primary objective of the warehouse management system, three factors of success, can only be achieved if the resources at ground level are well equipped and well informed to efficiently perform the warehouse tasks.
In order to facilitate the data capture right at the source, to customize the workflow for the resources (manpower/machines) and to transmit and share the real-time inventory data between the central workstations and resources, RFID devices, which can be held in hand or mounted on machinery (forklifts and stalker cranes), are widely used in present-day warehouses.
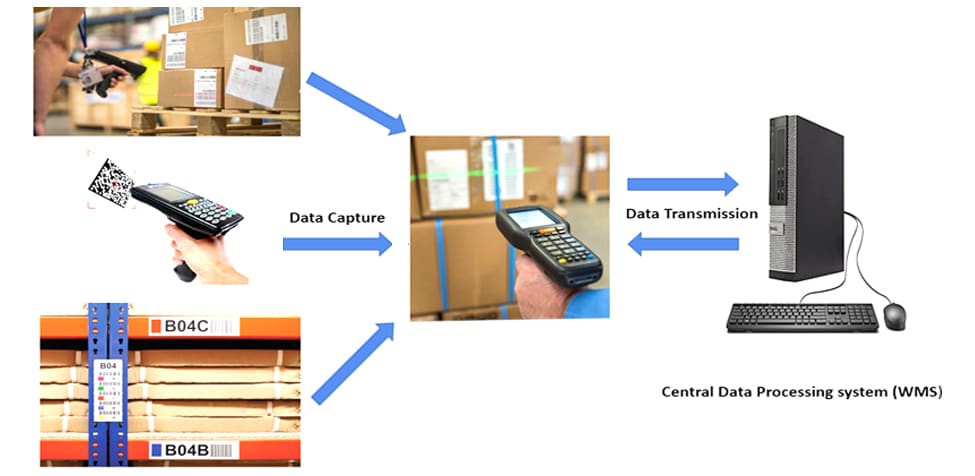
Data capture and transmission through RFID devices
To work with mobile data capture devices, all the inventory and elements of the warehouse structure, like staging areas, work centers, and storage bins, have to be coded and labeled with a 2-dimensional bar code or QR code that holds the information relevant to the element.
Radio-frequency scanning devices, which can have a wireless connection through WI-FI, Bluetooth, or other data transmission technologies like 3G and 4G, will be connected to the central data processing system (warehouse management system) and facilitate the real-time data transmission across the systems in the warehouse.
Data that is captured either through the scanning function or by entering it manually right into the device gets transmitted and updated in the central data processing system (warehouse management system) because of the live communication between the two.
The radio frequency framework functionality of EWM, which consists of logical transactions, function codes, and validation objects, designs the necessary framework for the RFID devices to navigate through workflows during the execution of warehouse tasks.
The radio frequency framework usually works in coordination with the resource management functionality of the warehouse management system to assign executable packages to the resources based on the resources’ capabilities.
As the devices are connected to the central data processing system in real-time, the instructions about the task to be executed according to the automated workflow will be communicated to the personalized handheld devices. Upon confirmation of assigned task completion, instructions for the next task in line will be displayed on the screen of the mobile device.
RF devices in action
The use of mobile devices in the task execution process is widely adopted for almost every activity in the warehouse.
During the goods receipt posting, an RF scanner facilitates the receipt of the inbound delivery items through Handling Units. That means, instead of checking for inbound delivery items from a pile of packages in the staging area, HUs can be received randomly by scanning the labels printed on them. A simple scan of the label will update the system with details of the products in it, their quantity, country of origin, etc.
During the Putaway and Picking, warehouse tasks created from automated workflows will be assigned to the resources, and once the resource logs onto the respective device based on the pre-configured control parameters like resource group, personalization profile, and queue assignment, the RF interface guides the resource with instructions to execute the goods movement tasks in sequence.
For example, if the HU needs to be Putaway from the staging area to the destination bin, then the instructions about the source HU, source bin, and system-proposed destination bin will be presented to the resource on his RF device screen in the form of validation fields. Validation of the destination bin by scanning the 2D barcode or QR code on the destination bin signals the task’s completion and displays the instructions for another task in sequence.
Depending upon the warehouse task being performed, the screens of the RFID devices will be presented with necessary manual entry fields, validation fields, function codes, and push buttons.
The same is true for other warehousing processes such as replenishment, physical inventory counting, and ad-hoc warehouse tasks such as bin-to-bin inventory transfer, among others.
Advantages of using RF devices in warehouses
- Increased productivity as the data related to task execution is readily available for processing at each individual resource level without having to refer to the fixed workstations
- Real-time data updates through scanning result in data accuracy throughout the system
- Improved visibility of inventory through real-time inventory updates
- Accelerated order fulfillment as the resources are guided seamlessly through the picking, packing, and loading tasks
- Cost savings through efficient resource management
Conclusion
The use of RFID devices certainly drives warehouse operations at an optimum pace, aids in maintaining data accuracy, and improves overall productivity through effective resource utilization.
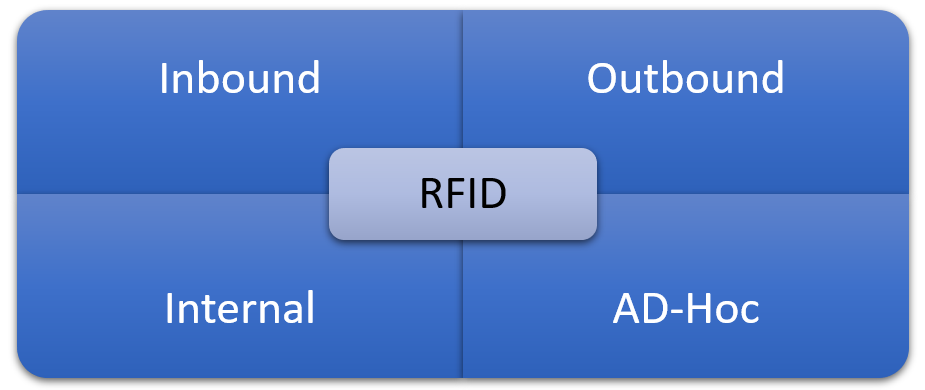
RFID devices rely on the radio frequency framework to execute transactions in warehouses. Thanks to SAP EWM’s built-in RF framework, in which the logical transactions and screens can be customized with respect to the business process requirements, menus can be personalized for the users based on the nature of tasks they are assigned, like inbound processing tasks, outbound processing tasks, and/or internal processing tasks.
Domain knowledge of warehousing, expertise on warehouse management system functionality and its integration with ERP systems, and expertise in various phases of functional testing are essential to successfully design, test, and deploy the appropriate framework for RFID devices.
Cigniti, the world’s leading AI & IP-led Digital Assurance and Digital Engineering Services company can be a valued partner throughout your journey of designing and deploying a suitable RF framework for your mobile data capturing devices.





Leave a Reply